Criminals of the worst kind!!!
1 of 2:
YouTube Added: 14.10.2009
2 of 2:
YouTube Added: 14.10.2009
The man who trades freedom for security does not deserve nor will he ever receive either. – Benjamin Franklin
Immortality!
Related information:
Dr. Bruce Lipton is a former medical school professor and research scientist:
– Dr. Bruce Lipton Ph.D. – Changing Our Cells by Thought
– Bruce Lipton – The New Biology – Where Mind and Matter Meet
(I highly recommended this video. This will change your life. If you do not want to change and stay all the same, then don’t you dare watching it!)
The following books are not about religion, sects, cults, gurus or new age channels:
– Life and Teaching of the Masters of the Far East, Vol. 1 Price: $8.76
– Life and Teaching of the Masters of the Far East, Vol. 2 Price: $10.95
– Life and Teaching of the Masters of the Far East, Vol. 3 Price: $10.95
In German:
– Leben und Lehren der Meister in Fernen Osten. Band 1-3 Preis: EUR 12,95
Proof that miraculous abilities are indeed real:
– China’s Super Psychics (At the moment this book (in English) is only available at ridiculous prices.)
In German:
– Indigo-Schulen: Trainingsmethoden für medial begabte Kinder Preis: EUR 8,95
(The German title is complete BS. ‘Super Psychics’ is a lot better, but would you have guessed that this includes healing abilities, teleportation, biolocation and manifesting out of thin air etc.?)
Watch also:
– Ling Kong Jing (Empty Force) Demo by Master Shr on Bill Moyers Special
– Qigong master (Realy cool Must see! ): (This master appears to be mentally unstable but he has great abilities.)
– Qigong Master Boils Water With His Hands Pyrokinesis
My Tai Chi and Qi Gong teachers can also do the ‘miraculous’. For them it’s ‘normal’. They can perform Ling Kong Jing (Empty Force) at any given distance. Such abilities are real.

Pictures of the winners of the Nobel Prize in medicine, from left, Elizabeth Blackburn, Carol Greider and Jack Szostak, are displayed on a screen at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm (AFP)
Oct. 5 (Bloomberg) — Three American scientists won the Nobel Prize in medicine for research on cell division and the “immortality enzyme” that can help cells multiply without damage, illuminating conditions including cancer and aging.
Elizabeth Blackburn, 60, a professor at the University of California in San Francisco; Carol Greider, 48, a professor at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore; and Jack Szostak, 56, a professor at Harvard Medical School in Boston, will share the 10 million-Swedish kronor ($1.4 million) prize equally, the Nobel Assembly said today in Stockholm. It’s the first time two women have jointly won the prize.
Their research explored a fundamental question of life: how chromosomes that carry the genetic code in DNA are copied in their entirety each time a cell divides. The key is the end of the chromosome, where caps known as telomeres reside. An enzyme discovered by the researchers, dubbed telomerase, prevents the end from being shaved off and maintains the health of the cell as it replicates — earning it the title of “immortality enzyme.”
“This is this really a tribute to curiosity-driven basic science,” Greider said today at a press conference at the Johns Hopkins campus with her two children, ages 9 and 13, in the audience. “We were just interested in the fundamental question of cell biology.”

“I expected a reaction but not such a violent one.”
“If I know something, I will not shut my mouth.”
In April 2009 Andrés Carrasco, an Argentinian embryologist, gave an interview to the leading Buenos Aires newspaper Página 12, in which he described the alarming results of a research project he is leading into the impact of the herbicide glyphosate on the foetuses of amphibians. Dr Carrasco, who works in the Ministry of Science’s Conicet (National Council of Scientific and Technical Investigations), said that their results suggested that the herbicide could cause brain, intestinal and heart defects in the foetuses. Glyphosate is the herbicide used in the cultivation of Monsanto’s genetically modified soya, which now covers some 18 million hectares, about half of Argentina’s arable land. [1]
Carrasco said that the doses of herbicide used in their study were “much lower than the levels used in the fumigations”. Indeed, as some weeds have become resistant to glyphosate, many farmers are greatly increasing the concentration of the herbicide. According to Página 12, this means that, in practice, the herbicide applied in the fields is between 50 and 1,540 times stronger than that used by Carrasco. The results in the study are confirming what peasant and indigenous communities – the people most affected by the spraying – have been denouncing for over a decade. The study also has profound consequences for the USA’s anti-narcotics strategy in Colombia, because the planes spray glyphosate, reinforced with additional chemicals, on the coca fields (and the peasants living among them).
Three days after the interview, the Association of Environmental Lawyers filed a petition with the Argentine Supreme Court, calling for a ban on the use and sale of glyphosate until its impact on health and on the environment had been investigated. Five days later the Ministry of Defence banned the planting of soya in its fields. This sparked a strong reaction from the multinational biotechnology companies and their supporters. Fearful that their most famous product, a symbol of the dominant farming model, would be banned, they mounted an unprecedented attack on Carrasco, ridiculing his research and even issuing personal threats. He was accused of inventing his whole investigation, as his results have not yet been peer-reviewed and published in a prestigious scientific journal.
Read moreScientist: Monsanto’s herbicide could cause brain, intestinal and heart defects in foetuses
‘Criminals’ includes governments & intelligences.

The findings threaten to undermine the key forensic technique, which has secured thousands of convictions in Britain and around the world.
In experiments, a team of Israeli scientists were able to obliterate all traces of DNA from a blood sample and add someone else’s genetic material in its place.
The process was so successful that it fooled forensic scientists who carry out DNA fingerprinting for American courts.
The findings threaten to undermine the key forensic technique, which has secured thousands of convictions in Britain and around the world.
It demonstrates that, in theory, criminals could plant samples of blood or saliva at crime scenes to cover their tracks while leading to innocent people being wrongly convicted.
Dr Dan Frumkin, who led the research, said: “If you can fake blood, saliva or any other tissue, you can engineer a crime scene.
“You have full control of the situation. Any biology undergraduate could perform this.”
Read moreStudy: DNA can be faked by criminals, crime scene can be engineered
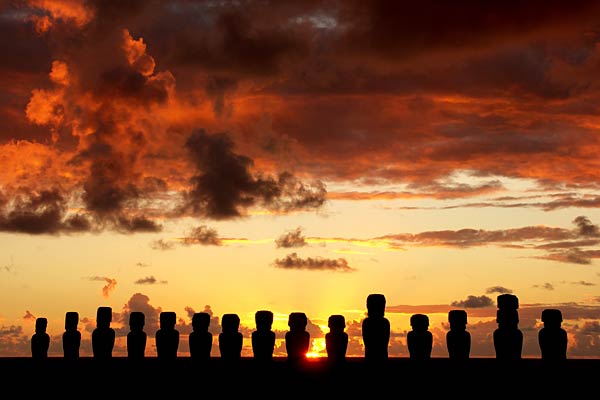

(NaturalNews) No one can argue that Easter Island, located off the coast of Chile in the South Pacific, is one of the most mysterious places on earth. The extremely remote island is home to huge, enigmatic monoliths carved by the one-time inhabitants of the island who settled there over 1,500 years ago. The large-eyed stone figures stare out at the sea as if guarding a secret. Now scientists have uncovered another mystery of Easter Island — one that could be important for the future of humankind. New research suggests that a natural compound found in the soil of the island could be a health-promoting elixir of long life.
If this sounds like a fantasy or hocus pocus, it isn’t. In fact, a study of the compound was just published in the prestigious science journal Nature. Researchers say the biochemical, produced by soil bacteria, has such extraordinary life-extending properties it could lead to a genuine “anti-aging” pill that keeps people young.
Scientists at the University of Texas (UT) Health Science Center at San Antonio and collaborating centers at the University of Michigan at Ann Arbor and Jackson Laboratory in Bar Harbor, Maine, gave the Easter Island compound, which is called rapamycin after the island’s Polynesian name Rapa Nui, to middle-aged mice who were the equivalent, in mice years, of 60 year old people. The compound increased the animals’ expected by 28 percent to 38 percent. Place in human perspective, the scientists noted this increase in lifespan would be greater than the predicted increase in extra years of life if all cancers and heart disease could be prevented and cured.
“We believe this is the first convincing evidence that the aging process can be slowed…,” said Randy Strong, Ph.D., who directs the National Institute on Aging (NIA) funded Aging Interventions Testing Center in San Antonio. He is a professor of pharmacology at the UT Health Science Center and a senior research career scientist with the South Texas Veterans Health Care System.
Read moreEaster Island Mystery: Scientists Say Natural Compound on Island Extends Lifespan

Abdel Halim Tolba, a snake hunter, holds a mouse which is used to feed snakes at the Tolba snake farm in Cairo, Egypt. (REUTERS)
HONG KONG (Reuters) – Chinese researchers have managed to create powerful stem cells from mouse skin and used these to generate fertile live mouse pups.
They used induced pluripotent skin cells, or iPS cells — cells that have been reprogrammed to look and act like embryonic stem cells. Embryonic stem cells, taken from days-old embryos, have the power to morph into any cell type and, in mice, can be implanted into a mother’s womb to create living mouse pups.
Their experiment, published in Nature, means that it is theoretically possible to clone someone using ordinary connective tissue cells found on the person’s skin, but the experts were quick to distance themselves from such controversy.
“We are confident that tremendous good can come from demonstrating the versatility of reprogrammed cells in mice, and this research will be used to … understand the root causes of disease and lead to viable treatments and cures of human afflictions,” said Fanyi Zeng of the Shanghai Institute of Medical Genetics at Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
“It would not be ethical to attempt to use iPS cells in human reproduction. It is important for science to have ethical boundaries,” she said, adding that their study was “in no way meant as a first step in that direction.”
(NaturalNews) Colostrum has been called the promise of life. It is the first food, in which all the immune and growth factors that insure health and vitality are transferred from the mother to the newborn. Research has shown that colostrum is the one supplement that can bring help to everyone that uses it, largely because of its ability to perform many of the functions of human growth hormone (HGH) in the body. Many scientists believe colostrum may be the most important preventative that can be consumed by a mammal. The value of colostrum has been documented in clinical observations and is supported by a large database. A team of scientists in London has now found that colostrum can prevent the death of human neurons and effectively treat Alzheimer’s patients. While this was going on, another research team was documenting that colostrum knocks out intestinal inflammation.
Scientists at St. George’s University had already demonstrated that colostrinin, a proline-rich polypeptide isolated from colostrum, can effectively treat Alzheimer’s disease patients. In a new study, they investigated whether colostrinin has effects on the aggregation and toxicity of beta-amyloid, the main constituent of plaque in the brain believed to be the cause of Alzheimer’s disease.
Read moreReverse the Aging Process: Colostrum Functions Like Human Growth Hormone
Related articles:
– Airborne fungus Ug99 threatens global wheat harvest (The Guardian):
“The US army produced wheat rust as part of its biological weapons programme in the 1960s.”
– UN alert: One-fourth of world’s wheat at risk from new fungus (World Tribune)
– Billions at risk from wheat super-blight (New Scientist)

Oregon State scientist Mary Verhoeven is among those working to develop wheat varieties resistant to a strain of “stem rust” that a colleague calls “a time bomb.”
The Ug99 fungus, called stem rust, could wipe out more than 80% of the world’s wheat as it spreads from Africa, scientists fear. The race is on to breed resistant plants before it reaches the U.S.
The spores arrived from Kenya on dried, infected leaves ensconced in layers of envelopes.
Working inside a bio-secure greenhouse outfitted with motion detectors and surveillance cameras, government scientists at the Cereal Disease Laboratory in St. Paul, Minn., suspended the fungal spores in a light mineral oil and sprayed them onto thousands of healthy wheat plants. After two weeks, the stalks were covered with deadly reddish blisters characteristic of the scourge known as Ug99.
Nearly all the plants were goners.
Crop scientists fear the Ug99 fungus could wipe out more than 80% of worldwide wheat crops as it spreads from eastern Africa. It has already jumped the Red Sea and traveled as far as Iran. Experts say it is poised to enter the breadbasket of northern India and Pakistan, and the wind will inevitably carry it to Russia, China and even North America — if it doesn’t hitch a ride with people first.
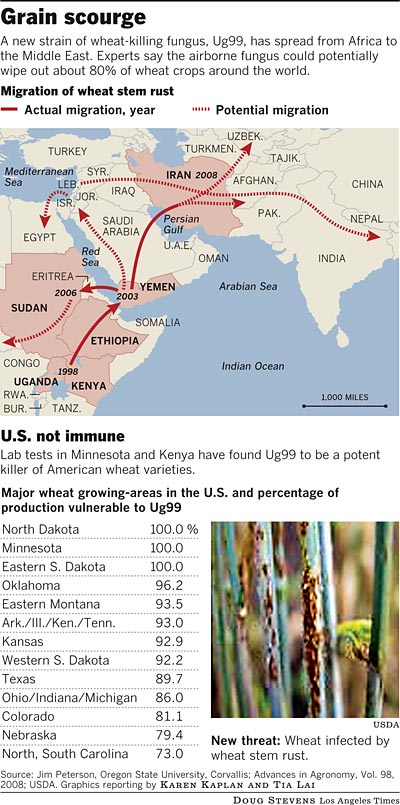
“It’s a time bomb,” said Jim Peterson, a professor of wheat breeding and genetics at Oregon State University in Corvallis. “It moves in the air, it can move in clothing on an airplane. We know it’s going to be here. It’s a matter of how long it’s going to take.”
Added: Mai 14, 2009
Source: YouTube
Related article: Winnipeg researcher charged with smuggling Ebola material into U.S.

A member of the research team in one of the modules where the experiment will take place Photograph: Pavel Zelensky/AFP/Getty Images
In a car park not so far away … It is a big brother experiment like no other, an experiment which will boldly go where few have gone – or probably wanted to go – before.
Six apparently fearless volunteers are to take part in a unique test by being locked up in what amounts to a series of small steel tins off a parking lot in Moscow for 105 days as scientists simulate a space rocket ride to Mars.
On Tuesday the team will step into a chain of cramped metal capsules, connected by cables and corrugated metal pipes, in a hangar at the back of the Institute of Medical and Biological Problems (IMBP) in the Russian capital, swing close the hatch and “blast off”.
The idea is for the 550 cubic-metre “ground exploration complex” (GEC) to recreate as closely as possible the atmosphere of a spacecraft racing through the solar system, bombarded by cosmic radiation. Any return flight to Mars – at least 34 million miles from our planet – would take between 18 months and three years, including landing and exploration.
The volunteers – four Russians, a French airline pilot and a German army engineer – will be kept under constant camera surveillance to record the physical and psychological impact of their time in the isolation chamber.
 An MRI scan of the brain of a multiple sclerosis sufferer |
Multiple sclerosis could be prevented through daily vitamin D supplements, scientists told The Times last night.
The first causal link has been established between the “sunshine vitamin” and a gene that increases the risk of MS, raising the possibility that the debilitating auto-immune disease could be eradicated.
George Ebers, Professor of Clinical Neurology at the University of Oxford, claimed that there was hard evidence directly relating both genes and the environment to the origins of MS.
His work suggests that vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy and childhood may increase the risk of a child developing the disease.
He has also established the possibility that genetic vulnerability to MS, apparently initiated by lack of vitamin D, may be passed through families.
These risks might plausibly be reduced by giving vitamin D supplements to pregnant woman and young children.
“I think it offers the potential for treatment which might prevent MS in the future,” Professor Ebers said.
“Our research has married two key pieces of the puzzle. The interaction of vitamin D with the gene is very specific and it seems most unlikely to be a coincidence of any kind.”
Warnings over sun exposure could now also be called into question – sunlight allows the body to produce the vitamin.
Read moreVitamin D is ray of sunshine for multiple sclerosis patients
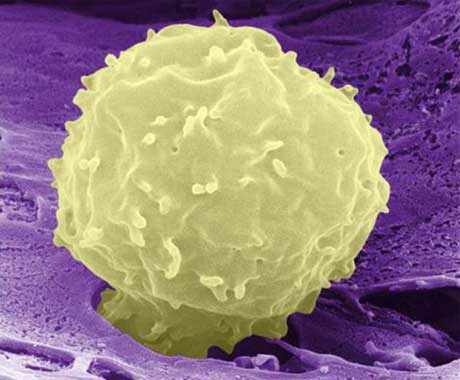
A stem cell emerging from rat bone marrow. By stimulating the release of stem cells after a heart attack, the healing process could be accelerated. Photograph: Imperial College London
A groundbreaking medical treatment that could dramatically enhance the body’s ability to repair itself has been developed by a team of British researchers.
The therapy, which makes the body release a flood of stem cells into the bloodstream, is designed to heal serious tissue damage caused by heart attacks and even repair broken bones. It is expected to enter animal trials later this year and if successful will mark a major step towards the ultimate goal of using patients’ own stem cells to regenerate damaged and diseased organs.
‘This would allow bodies to heal themselves’ Link to this audio
When the body is injured, bone marrow releases stem cells that home in on the damaged area. When they arrive, they start to grow into new tissues, such as heart cells, blood vessels, bone and cartilage.
Scientists already know how to make bone marrow release a type of stem cell that can only make fresh blood cells. The technique is used to collect cells from bone marrow donors to treat people with the blood cancer leukaemia.
Read moreRevolutionary stem cell therapy boosts body’s ability to heal itself
Steven Spielberg’s Jurassic Park film may have been pure science fiction – but extinct creatures such as Neanderthals to Sabre-toothed tigers could soon be brought back to life thanks to advances in DNA technology.

A scene from Jurassic Park III – maybe not too far from the truth
The idea of resurrecting extinct animals moved a step closer to reality last year when scientists announced that they had decoded almost all of the genome of the woolly mammoth, from 60,000-year-old remains found frozen in Siberia.
Now New Scientist magazine has named the 10 other beasts most likely to rise again, including the Irish elk deer whose antlers measured 12 feet across, the dodo and Neanderthal man.
Animals that died out thousands of years ago could be recreated using genetic information retrieved from well-preserved specimens recovered from permafrost, dark caves or dry desserts.
Read moreExtinct animals could be brought back to life thanks to advances in DNA technology
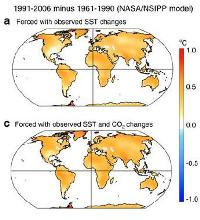 Figures from the Compo and Sardeshmukh study |
As dignitaries from around the world gather for the United Nations Climate Change Conference, attendees are unlikely to champion a recent study that demonstrates oceanic heat levels – and not man-made greenhouse gases – are to blame for increases in temperature on land.
An estimated 9,000 government, media and U.N. officials are meeting in Poznan, Poland, for the conference, discussing possible international action to combat global warming. According to media relations information provided by the conference, “Climate change is already happening, is unequivocal and this change can now be firmly attributed to human activity.”
Not so fast, says a study released earlier this year by Gilbert Compo and Prashant Sardeshmukh of the University of Colorado and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and presented in the scientific journal Climate Dynamics.
According to Compo and Sardeshmukh’s study, all the greenhouse gases humans have dumped in the atmosphere over the last 46 years – the primary factor most climate change proponents cite to blame humans for global warming – haven’t affected land temperatures at all.
The rise in land temperatures, the study states, can be tied directly to increased heat and humidity coming from warmer oceans, which in turn, the study admits, may be caused solely by natural forces.
Researchers have created the world’s thinnest sheet – a single atom thick – and used it to create the world’s smallest transistor, marking a breakthrough that could spark the development of super-fast computer chips.
This innovation will allow ultra small electronics to take over when the current silicon-based technology runs out of steam, according to Prof Andre Geim and Dr Kostya Novoselov from the University of Manchester.
They reveal details of transistors that are only one atom thick and fewer than 50 atoms wide in the journal, Nature Materials.
How “shocking”!?
Human beings have killed each other by the millions on this planet because they were ordered to do so.

A U.S. soldeir walks between cells at Abu Ghraib prison outside Baghdad in a 2004 photo. REUTERS/Damir Sagolj
WASHINGTON (Reuters) – Some things never change. Scientists said on Friday they had replicated an experiment in which people obediently delivered painful shocks to others if encouraged to do so by authority figures.
Seventy percent of volunteers continued to administer electrical shocks — or at least they believed they were doing so — even after an actor claimed they were painful, Jerry Burger of Santa Clara University in California found.
“What we found is validation of the same argument — if you put people into certain situations, they will act in surprising, and maybe often even disturbing, ways,” Burger said in a telephone interview. “This research is still relevant.”
Burger was replicating an experiment published in 1961 by Yale University professor Stanley Milgram, in which volunteers were asked to deliver electric “shocks” to other people if they answered certain questions incorrectly.
Milgram found that, after hearing an actor cry out in pain at 150 volts, 82.5 percent of participants continued administering shocks, most to the maximum 450 volts.
The experiment surprised psychologists and no one has tried to replicate it because of the distress suffered by many of the volunteers who believed they were shocking another person.
“When you hear the man scream and say, ‘let me out, I can’t stand it,’ that is the point when the real stress that people criticized Milgram for kicked in,” Burger said.
“It was a very, very, very stressful experience for many of the participants. That is the reason no one can ethically replicate the experiment today.”
ScienceDaily (Dec. 18, 2008) – A team led by International Arctic Research Center scientist Igor Semiletov has found data to suggest that the carbon pool beneath the Arctic Ocean is leaking.
The results of more than 1,000 measurements of dissolved methane in the surface water from the East Siberian Arctic Shelf this summer as part of the International Siberian Shelf Study show an increased level of methane in the area. Geophysical measurements showed methane bubbles coming out of chimneys on the seafloor.
“The concentrations of the methane were the highest ever measured in the summertime in the Arctic Ocean,” Semiletov said. “We have found methane bubble clouds above the gas-charged sediment and above the chimneys going through the sediment.”
Read moreScientists Find Increased Methane Levels In Arctic Ocean
1. Vitamin B3 cannot be patented.
2. Vitamin B3 is incredibly cheap.
3. If taken correctly there are no side effects.
3. Vitamin B3 might cure the disease.
That is the ultimate worst case scenario for ‘Big Pharma’ and it’s salesman (= doctors).
(There are still great doctors out there but for many reasons their numbers are decreasing dramatically.)
There are a lot of junk science studies circulating out there that now want to tell us that vitamins have no effect.
Look who conducted the study and on whose payroll they are. There are only around 5% independent scientists out there. The other 95% are ‘bought’ by corporations. Any disease ‘can’ be cured with Alternative Medicine.
___________________________________________________________________________
(OMNS, December 9, 2008) The news media recently reported that “huge doses of an ordinary vitamin appeared to eliminate memory problems in mice with the rodent equivalent of Alzheimer’s disease.” They then quickly added that “scientists aren’t ready to recommend that people try the vitamin on their own outside of normal doses.” (1)
In other words, extra-large amounts of a vitamin are helpful, so don’t you take them!
That does not even pass the straight-faced test. So what’s the story?
Researchers at the University of California at Irvine gave the human dose equivalent of 2,000 to 3,000 mg of vitamin B3 to mice with Alzheimer’s. (2) It worked. Kim Green, one of the researchers, is quoted as saying, “Cognitively, they were cured. They performed as if they’d never developed the disease.”
Specifically, the study employed large amounts of nicotinamide, the vitamin B3 widely found in foods such as meat, poultry, fish, nuts and seeds. Nicotinamide is also the form of niacin found, in far greater quantity, in dietary supplements. It is more commonly known as niacinamide. It is inexpensive and its safety is long established. The most common side effect of niacinamide in very high doses is nausea. This can be eliminated by taking less, by using regular niacin instead, which may cause a warm flush, or choosing inositol hexaniacinate, which does not. They are all vitamin B3.
HealthDay Reporter mentioned how cheap the vitamin is; the study authors “bought a year’s supply for $30” and noted that it “appears to be safe.” Even so, one author said that “I wouldn’t advocate people rush out and eat grams of this stuff each day.” (1)
Source: YouTube
The Biology of Belief is a groundbreaking work in the field of New Biology.
Author Dr. Bruce Lipton is a former medical school professor and research scientist.
His experiments, and that of other leading edge scientists, have examined in great detail the processes by which cells receive information. The implications of this research radically change our understanding of life.
It shows that genes and DNA do not control our biology; that instead DNA is controlled by signals from outside the cell, including the energetic messages emanating from our positive and negative thoughts.
Dr. Lipton’s profoundly hopeful synthesis of the latest and best research in cell biology and quantum physics is being hailed as a major breakthrough showing that our bodies can be changed as we retrain our thinking.
The Biology of Belief: Unleashing the Power of Consciousness, Matter, & Miracles
by Bruce H. Lipton (Hardcover – Sep 15, 2008)
A revolutionary device that can harness energy from slow-moving rivers and ocean currents could provide enough power for the entire world, scientists claim.

Existing technologies require an average current of five or six knots to operate efficiently, while most of the earth’s currents are slower than three knots Photo: AP
The technology can generate electricity in water flowing at a rate of less than one knot – about one mile an hour – meaning it could operate on most waterways and sea beds around the globe.
UXBRIDGE, Canada – An apparent rapid upswing in ocean acidity in recent years is wiping out coastal species like mussels, a new study has found.
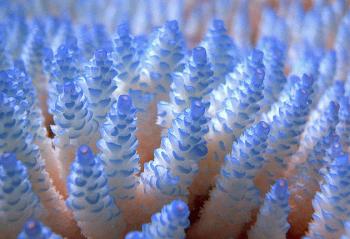
Coral at the Great Barrier Reef. Rising carbon dioxide levels in the world’s oceans due to climate change, combined with rising sea temperatures, could accelerate coral bleaching, destroying some reefs before 2050, said an Australian study in January 2002. (Reuters)
“We’re seeing dramatic changes,” said Timothy Wootton of the Department of Ecology and Evolution at the University of Chicago, lead author of the study published Monday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The study shows increases in ocean acidity that are more than 10 times faster than any prediction.
“It appears that we’ve crossed a threshold where the ocean can no longer buffer the effects of CO2 in the atmosphere,” Wootton told IPS.

The journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step. – Lao Tzu
A naturally occuring substance that can create “immortal cells” could be the key to finding a real elixir of youth, scientists claim.
Researchers believe boosting the amount of a naturally forming enzyme in the body could prevent cells dying and so lead to extended, healthier, lifespans..
The protein telomerase helps maintain the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes which act like the ends of shoelaces and stop them unravelling.
As we age, and our cells divide, these caps become frayed and shorter and eventually are so damaged that the cell dies. Scientists believe boosting our natural levels of telomerase could rejuvenate them.
A team at the Spanish National Cancer Centre in Madrid tested the theory on mice and found that those genetically engineered to produce 10 times the normal levels of telomerase lived 50 per cent longer than normal.
Read moreScientists take a step closer to an elixir of youth

A mountain in the eastern Hellas region of Mars
Huge glaciers up to half a mile thick have been discovered close to the equator of Mars and are thought to be the remnants of an ice age on the planet.
The glaciers are thought to have been formed up to 100 million years ago and are the “most dramatic” evidence yet of climate change on Mars.
Hundreds of glaciers have been identified by researchers using ground-penetrating radar that allows them to see through a rocky layer of debris covering the ice.
The biggest of the glaciers are up to 13 miles long and more than 60 miles wide and represent a potential source of water for astronauts on missions to Mars.

Claudia Castillo, the patient in the ground-breaking operation. Photo: AP
PARIS — Physicians at four European universities have completed what they say is the first successful transplant of a human windpipe using a patient’s own stem cells to fashion an organ and prevent its rejection by her immune system, according to an article in the British medical journal The Lancet. One of the physicians said the surgery could herald a “new age in surgical care.”
The transplant operation was performed on the patient, Claudia Castillo, in June in Barcelona, Spain, to alleviate an acute shortage of breath caused by a failing airway following severe tuberculosis. It followed weeks of preparation carried out at the universities of Barcelona, Spain, Bristol, England and Padua and Milan in Italy.