The federal prison in Florence, Colo., has long held terrorists. The justice system has absorbed a surge of terrorism cases since 2001 without the international criticism that Guantánamo Bay has attracted.
– Beyond Guantánamo, a Web of Prisons for Terrorism Inmates (New York Times, Dec. 10, 2011)
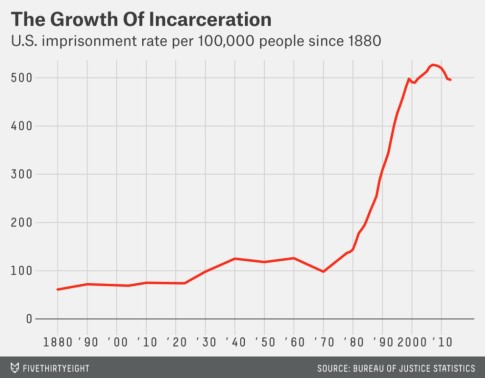
WASHINGTON — It is the other Guantánamo, an archipelago of federal prisons that stretches across the country, hidden away on back roads. Today, it houses far more men convicted in terrorism cases than the shrunken population of the prison in Cuba that has generated so much debate.
An aggressive prosecution strategy, aimed at prevention as much as punishment, has sent away scores of people. They serve long sentences, often in restrictive, Muslim-majority units, under intensive monitoring by prison officers. Their world is spare.
Among them is Ismail Royer, serving 20 years for helping friends go to an extremist training camp in Pakistan. In a letter from the highest-security prison in the United States, Mr. Royer describes his remarkable neighbors at twice-a-week outdoor exercise sessions, each prisoner alone in his own wire cage under the Colorado sky. “That’s really the only interaction I have with other inmates,” he wrote from the federal Supermax, 100 miles south of Denver.
There is Richard Reid, the shoe bomber, Mr. Royer wrote. Terry Nichols, who conspired to blow up the Oklahoma City federal building. Ahmed Ressam, the would-be “millennium bomber,” who plotted to attack Los Angeles International Airport. And Eric Rudolph, who bombed abortion clinics and the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta.
In recent weeks, Congress has reignited an old debate, with some arguing that only military justice is appropriate for terrorist suspects. But military tribunals have proved excruciatingly slow and imprisonment at Guantánamo hugely costly — $800,000 per inmate a year, compared with $25,000 in federal prison.
Read moreBeyond Guantánamo, A Web Of Prisons For Terrorism Inmates