Rahm Emanuel was only giving voice to widespread political wisdom when he said that a crisis should never be “wasted.” Crises enable vastly accelerated political agendas and initiatives scarcely conceivable under calmer circumstances. So it goes now.
Here we stand more than a year into a grave economic crisis with a projected budget deficit of 13% of GDP. That’s more than twice the size of the next largest deficit since World War II. And this projected deficit is the culmination of a year when the federal government, at taxpayers’ expense, acquired enormous stakes in the banking, auto, mortgage, health-care and insurance industries.
With the crisis, the ill-conceived government reactions, and the ensuing economic downturn, the unfunded liabilities of federal programs — such as Social Security, civil-service and military pensions, the Pension Benefit Guarantee Corporation, Medicare and Medicaid — are over the $100 trillion mark. With U.S. GDP and federal tax receipts at about $14 trillion and $2.4 trillion respectively, such a debt all but guarantees higher interest rates, massive tax increases, and partial default on government promises.
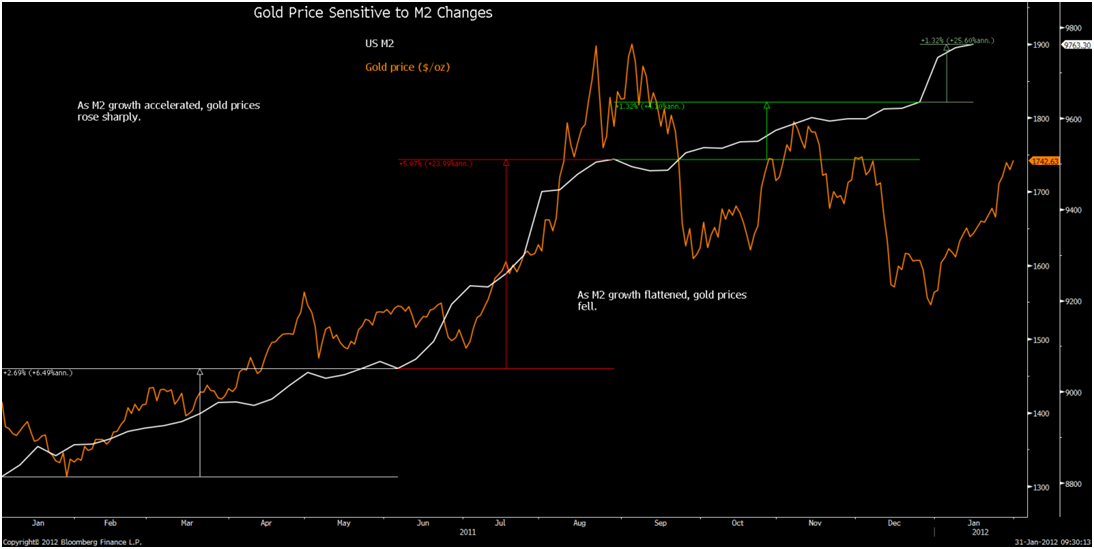
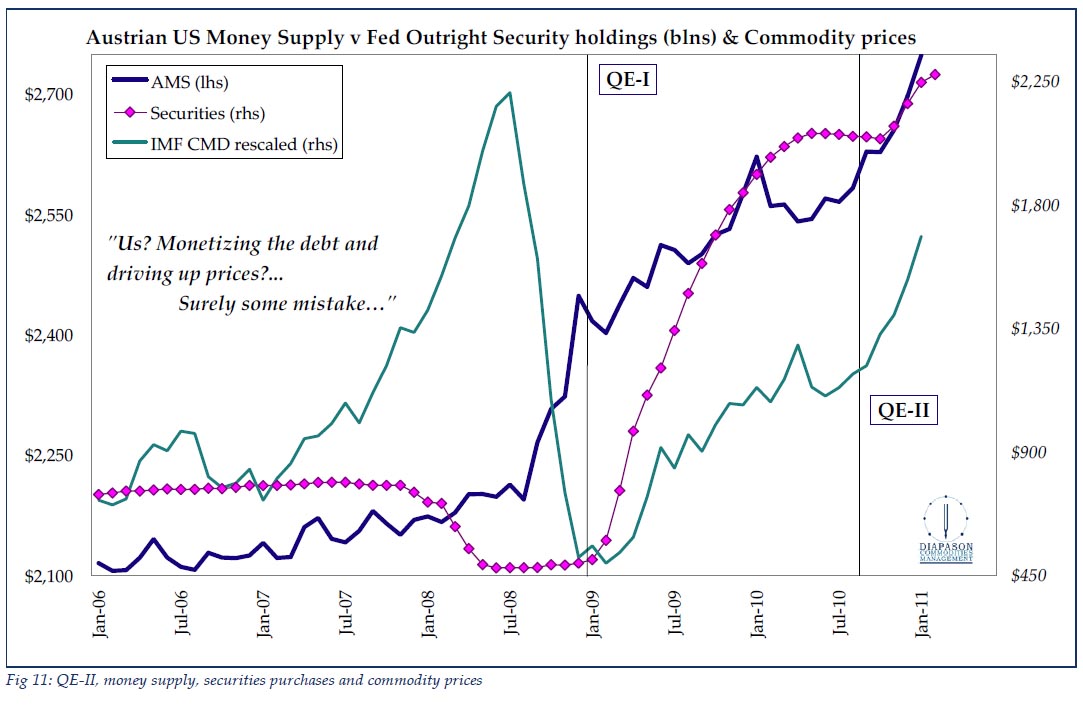
But as bad as the fiscal picture is, panic-driven monetary policies portend to have even more dire consequences. We can expect rapidly rising prices and much, much higher interest rates over the next four or five years, and a concomitant deleterious impact on output and employment not unlike the late 1970s.
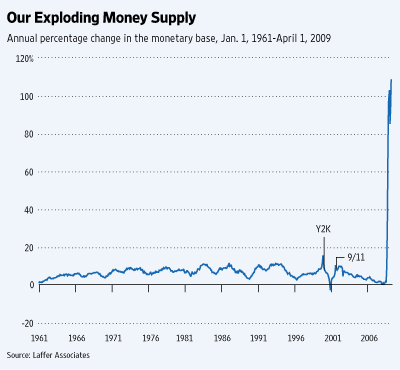
About eight months ago, starting in early September 2008, the Bernanke Fed did an abrupt about-face and radically increased the monetary base — which is comprised of currency in circulation, member bank reserves held at the Fed, and vault cash — by a little less than $1 trillion. The Fed controls the monetary base 100% and does so by purchasing and selling assets in the open market. By such a radical move, the Fed signaled a 180-degree shift in its focus from an anti-inflation position to an anti-deflation position.
The percentage increase in the monetary base is the largest increase in the past 50 years by a factor of 10 (see chart). It is so far outside the realm of our prior experiential base that historical comparisons are rendered difficult if not meaningless. The currency-in-circulation component of the monetary base — which prior to the expansion had comprised 95% of the monetary base — has risen by a little less than 10%, while bank reserves have increased almost 20-fold. Now the currency-in-circulation component of the monetary base is a smidgen less than 50% of the monetary base. Yikes!
Read moreGet Ready for Inflation and Higher Interest Rates: The unprecedented expansion of the money supply could make the ’70s look benign