“Could deposits below €100k be protected as it happened in Cyprus? The answer depends on the total amount of deposits above €100k. If there are enough of these large deposits above €100k, then most likely any required deposit haircut will be inflicted on these depositors only. There are no recent data on how big this universe of large deposits is. The most recent data from the European Commission suggest that at the end of 2012, covered (i.e. those below €100k) represented 75% of eligible Greek deposits. We suspect this number is now significantly higher leaving little room for depositors with less than €100k to be spared.“
You’ve been warned, Greece!
Here is what happened to Mexico:
– Hedge Fund Manager Kyle Bass Explains The New World Order (Panel Presentation):
On Greece:
For those who think a 50% write-down on debt will fix Greece, you have lost your mind. It is only a full wipe-out of the non-TROIKA-owned debt that is the only mathematical way for Greece to have any chance.
…
Don’t believe these governments when they tell you everything is going to fine. The day before Mexico devalued by 60% they denied that they would ever devalue. They can and will never tell you the truth. Find your own numbers.
Here is what happened to Belarus:
– Belarus Devalues Its Currency By 56% Overnight, Against Every Currency Out There:
Luckily for those who held their “money” in the form of gold and silver, they just got an instantaneous 56% value preservation and a relative boost in their purchasing power with just one central bank announcement.
– Will Greek Depositors Under €100,000 Be Spared In Case Of A “Bail-In” (ZeroHedge, July 4, 2015):
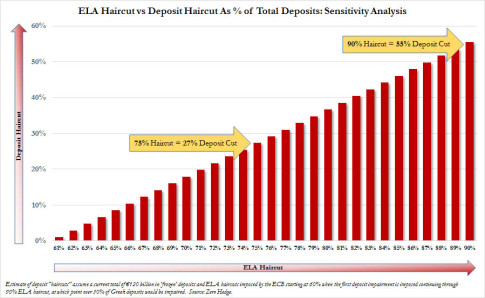
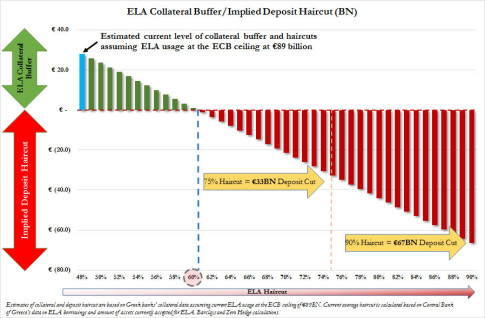
One week ago, we first explained that as the Cyprus bail-in “blueprint” scenario unfolds, the one final, and most important, remaining variable in the ongoing Greek drama, soon to devolve to tragedy, is how big the ECB’s ELA haircuts would be in the case of a No vote, which would be the first catalyst of a depositor haircut.
Then, overnight, in a report since denied by both the Greek finance ministry and by the European Banking Authority Plan, the pro-Europe FT did yet another hit piece on Greece desperate to push those Greek voters on the fence ahead of tomorrow’s referendum to vote “Yes” (just think of the lost advertising revenue if say Deutsche Bank were to go under).
Greek banks are preparing contingency plans for a possible “bail-in” of depositors amid fears the country is heading for financial collapse, bankers and businesspeople with knowledge of the measures said on Friday.
The plans, which call for a “haircut” of at least 30 per cent on deposits above €8,000, sketch out an increasingly likely scenario for at least one bank, the sources said.
Ignoring whether the FT is now merely a venue used by conflicted parties to publish pro-Europe, anti-Syriza hit piecestthat benefit “bankers and businesspeople with knowledge of the measures” and are promptly refuted, the article does bring up a relevant point: if the ECB does escalate the ELA collateral haircuts, something we analyzed in our own piece last week, what kind of haircut scenarios are possible, and will “insured” deposits under €100,000 be indeed made whole, or will the bail-in affect, as the FT suggested, everyone with over €8,000 in savings?
Regarding the first part of the question, what are the possible scenarios, JPM had this to say yesterday when evaluating the history of bail-ins in Europe in recent years:
If the deterioration in asset quality means there is no sufficient collateral to cover ELA claims, either the ECB (via its ELA residual claim) or domestic depositors will have to suffer a loss. Our understanding is that there are no clear rules on whether this ELA residual claim will be ranked above depositors or not. In fact EU policymakers adopted different and inconsistent approaches in the past when faced with bank insolvencies:
- In the case of Cypriot banks, depositors were hit while senior bond holders were spared, so seniority was not respected. ELA claims were also protected.
- Deposits of foreign branches were protected in the case of Cyprus while deposits of domestic branches were hit. This is the opposite of what happened to Iceland.
- In the case of Ireland, which also had a big banking system relative to the size of its economy, only sub debt holders, accounting for a very small portion of total creditors, were hit. No depositors were hit, in either domestic or foreign branches.
- In the case of SNS, sub debt holders were wiped out and reports suggest that the Dutch government came close to imposing losses on senior bond holders and was only prevented from doing so because of unsecured intergroup loans between SNS bank and Reaal insurance that would be subjected to the same losses as senior bond holders.
In other words, Europe will do what it always does: make it up as it goes alone. However, one notable difference between Cyprus and Greece is that the former held the deposits of a number of wealthy Russian oligarchs, which skewed the deposit distribution a la the 80/20 rule, and permitted smaller depositors to be saved while the Russians took the bulk of the hits (an outcome which according to some led to the suicide of Russian billionaire in exile, Boris Berezovsky).
Unlike Cyprus, Greece does not have the luxury of several massive depositors. In fact, according to JPM, the distribution of deposits appears to be relatively flat. JPM continues:
… under a stress scenario of prolonged impasse, Greek depositors will be likely hit while ELA claims are protected. There is currently €120bn of deposits with Greek banks. A haircut increase on ELA collateral assets from our currently estimated level of 43% to 60%, for example, would require a €26bn deposit haircut or 20% of outstanding bank deposits assuming for simplicity no available buffer from shareholders or bond holders. A bigger increase in the collateral haircut, for example to 75%, would require a €50bn deposit haircut or 40% of outstanding bank deposits.
Whereas we disagree with JPM’s calculation due to our baseline assumption that the current haircut level is more in the 48% region, we do agree with the directionality. As a reminder, this was our own math as laid out last week:
But what does this mean for ordinary Greeks, those who have negligible amounts still held by Greek banks despite our recurring pleas to withdraw their funds ahead of just this eventuality? Sadly, nothing good. Here is JPM’s conclusion:
Could deposits below €100k be protected as it happened in Cyprus? The answer depends on the total amount of deposits above €100k. If there are enough of these large deposits above €100k, then most likely any required deposit haircut will be inflicted on these depositors only. There are no recent data on how big this universe of large deposits is. The most recent data from the European Commission suggest that at the end of 2012, covered (i.e. those below €100k) represented 75% of eligible Greek deposits. We suspect this number is now significantly higher leaving little room for depositors with less than €100k to be spared. And the reserves that the Greek state has to back its bank deposit guarantee are miniscule, likely not more than a couple of billions euros.
Which means that unlike Cyprus, which was mostly a targeted punitive bail-in aimed almost entirely at Russian oligarchs, should the ECB indeed enact ELA haircuts which it may have to do as soon as Monday in the case of a No vote, it will be the ordinary Greeks who will see their already meager savings get haircut even more, anywhere between 30%, potentially up to 100% if the ECB were to announce the entire ELA no longer legal, pulls all funding and locks up Greek bank collateral.
Will the ECB do that? We don’t know, however Varoufakis’ gambit is simple: should the ECB engage the full Greek haircut it will incite an immediate panic and risks a run on other peripheral banks and the true spread of Greek contagion to Italy, Spain, Portugal and all other economically crushed countries where an anti-austerity politician is a frontrunner for the next leadership position. Such as France.