Scientists working on the world’s biggest machine are being besieged by phone calls and emails from people who fear the world will end next Wednesday, when the gigantic atom smasher starts up.
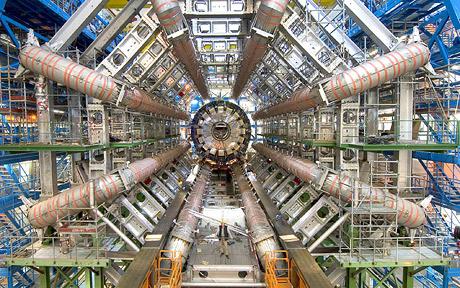
The Large Hadron Collider near Geneva, where particles will begin to circulate around its 17 mile circumference tunnel next week, will recreate energies not seen since the universe was very young, when particles smash together at near the speed of light.

Hadron Collider: The final pieces slot into place
Such is the angst that the American Nobel prize winning physicist Frank Wilczek of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has even had death threats, said Prof Brian Cox of Manchester University, adding: “Anyone who thinks the LHC will destroy the world is a t—.”
The head of public relations, James Gillies, says he gets tearful phone calls, pleading for the £4.5 billion machine to stop.
Read moreScientists get death threats over Large Hadron Collider